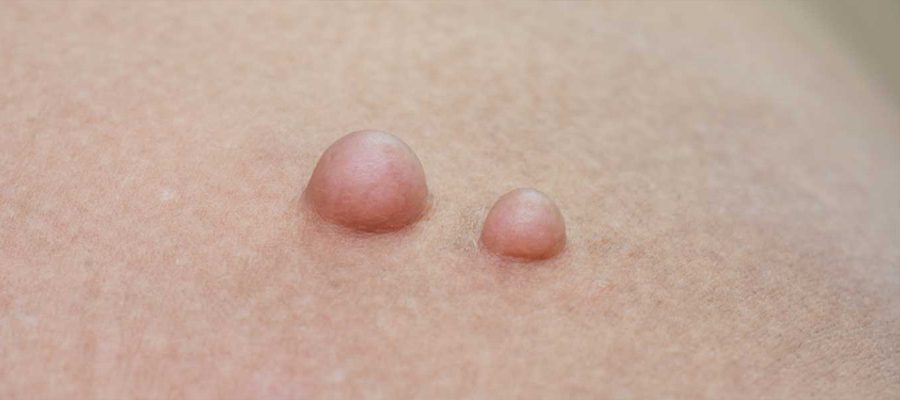
What is Liposuction?
Liposuction is the surgical removal of benign masses made up of fat cells, known medically as lipomas. Liposuction is usually harmless and occurs as soft and mobile masses under the skin. However, in some cases, removal may be necessary due to aesthetic concerns, pain or growth. This procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia and the entire fat tissue is removed with a simple surgical procedure. Liposuction can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly occurs on the back, neck, shoulders and arms. If a liposuction is enlarged, painful or at risk of infection, it is recommended that it be evaluated and removed by a doctor.
How is Fat Removal Performed?
The removal of the fat pad is usually done with a small, local surgical operation. First, the area is numbed with local anesthesia so that the patient does not feel pain. Then, the doctor makes a small incision and removes the fat pad along with its capsule. During the procedure, it is important to make sure that the entire fat pad is removed, because if the pad is not completely removed, it may grow back.
In some cases, if the fat pad is large or has spread into deeper tissues, a larger incision may be required and stitches may be required. For small fat pads, the incision scar is usually minimal and the healing process is rapid. The procedure takes an average of 15-30 minutes and the patient can usually return to normal life the same day. If there is anything suspicious in the removed pad, it may be sent to the laboratory for pathological examination.
When is Sebaceous Gland Dangerous?
Fat glands are usually harmless, but in some cases they may require medical attention. If the fat gland grows rapidly, hardens, causes pain, or puts pressure on surrounding tissues, it can be dangerous. Normally, fat glands are soft and mobile, but masses that become hard and adherent can be a sign of different health problems.
In addition, if there is a change in color, inflammation or an infected appearance on the skin surface, the sebaceous gland should definitely be seen by a doctor. In very rare cases, some sebaceous glands can be confused with malignant tumors. Therefore, a biopsy may be necessary, especially for rapidly growing or constantly changing sebaceous glands. If the sebaceous gland is pressing on important nerves or blood vessels in the body, surgical intervention may be necessary as it can cause functional problems.
What Happens If the Oil Cloth is Squeezed?
Squeezing the oil gland is definitely not recommended, as it can increase the risk of infection and inflammation. Since the oil glands are located in a capsule, the oil tissue inside them will not be completely removed when squeezed, and the capsule may even be damaged and grow larger. In addition, inflammation may develop under the skin as a result of the squeezing process and abscesses may form. This can be painful and require more complex medical intervention.
If the oil gland is causing discomfort or aesthetic concerns, it should definitely be removed by medical methods after consulting a doctor. The risk of recurrence of oil glands that have been surgically removed is very low, but if squeezed or treated incorrectly, the risk of growth and spread may increase.
How is it diagnosed?
The diagnosis of a fatty lump is usually made through a physical examination. The doctor will examine the lump manually to see if it is soft and mobile. In most cases, no additional testing is needed. However, if the lump is very large, has a hard structure, or is growing rapidly, imaging methods such as ultrasound or MRI may be used.
In some cases, a doctor may perform a biopsy to determine if the mass is benign. During the biopsy, a small tissue sample is taken for laboratory testing. If the lump is suspicious, further testing may be ordered. However, most lumps are harmless and can be removed easily with a simple surgical procedure.
What are the symptoms of sebaceous glands?
A sebaceous gland usually appears as a slowly growing, soft, and mobile mass under the skin. Most sebaceous glands are painless and can be felt as a distinct swelling on the skin surface. The main symptoms include:
Formation of a round or oval mass under the skin
Generally soft and easy to move
Slowly growing over time, but mostly stable
It is painless, but discomfort may be felt if it puts pressure on nerve tissues.
Causing aesthetic concerns depending on its size
In some cases, the sebaceous gland can become inflamed or infected. This can cause redness, swelling, tenderness, and occasionally pain. If the sebaceous gland is rapidly growing, hardened, or attached to surrounding tissue, a doctor should be consulted.
Why Does Sebaceous Gland Occur?
Sebaceous glands usually occur as a result of the accumulation of fat cells and the formation of an encapsulated tissue under the skin. Although the exact cause is not known, certain factors may predispose to the formation of sebaceous glands:
Genetic predisposition: It is more common in people with a family history of sebaceous glands.
Increased oil production in the skin: Excessive accumulation of fat cells and their inability to be eliminated by the body can cause the formation of oil glands.
Trauma or impact: Blows to the skin can cause fat cells to become trapped under the skin and, over time, form a lipoma.
Metabolic diseases: Conditions that affect metabolism, such as diabetes and thyroid diseases, can contribute to the formation of sebaceous glands.
Unhealthy diet and toxin accumulation: Unhealthy diet and toxin accumulation in the body can cause abnormal growth of fat cells.
Most sebaceous glands are harmless, but sebaceous glands that grow rapidly or become infected should be evaluated medically.
How is Non-Surgical Fat Removal Performed?
Non-surgical fat pad removal methods are generally applied to small and superficial fat pads. The most common methods are:
Laser treatment: Lasers can be used to break up small, superficial fat cells. This method is usually suitable for smaller lipomas.
Liposuction: A thin needle is inserted into the fat tissue and the fat tissue inside is sucked out. However, since the capsule surrounding the fat tissue is not completely removed in this method, there is a risk of recurrence.
Injection therapy: In some cases, certain chemicals can be injected into the sebaceous gland to cause it to shrink.
Non-surgical methods are generally suitable for small and painless fatty lumps. Surgical removal is the most permanent method for large lipomas or lipomas that press on nerve tissues.
Regions Where Sebaceous Glands Can Be Seen
Sebaceous glands can appear anywhere on the body, but the most common locations are:
Neck: It is seen as small and mobile swellings under the skin, especially in the neck area.
Back: It is one of the most common areas and can usually reach large sizes.
Shoulders: The fat glands under the skin can be easily felt in this area.
Arms and legs: May grow on muscles, but are usually painless.
Abdomen and groin area: Although rare, it can occur in these areas in some cases.
Face and scalp: Small oil glands may cause aesthetic concerns in these areas.
Sebaceous glands are generally harmless, but they may cause discomfort depending on their size and location.
Liposuction Prices 2025
Fat pad removal prices in 2025 may vary depending on the method to be applied, the size of the fat pad, the area where it is located, and the clinic where the procedure is performed. General price ranges are as follows:
Surgical procedures performed with local anesthesia for small fat glands: 3,000 TL – 10,000 TL
Surgical intervention for larger and deeper fat glands: 10,000 TL – 25,000 TL